Wage obligations under industrial agreements
In order to comply with wage obligations towards employees, an employer will need to understand the following:
Identifying the applicable
Identifying the correct rate of pay that applies to each of your employees is an essential part of ensuring wage compliance.
Once you have identified the industrial agreement that covers your employee’s employment and the employee’s classification under that agreement, the next step is identifying the correct rate of pay for the employee.
Under most industrial agreements an employee’s minimum rate of pay is outlined in a ‘minimum wage’ clause of the agreement. Click the magnifying glass for an example of such a clause.
Part-time and casual employees
Under most industrial agreements, employees who are casual or part-time are required to be paid a pro-rata amount of the minimum adult wage according to the hours of work they have performed.
Ordinary hours of work
Most industrial agreements will use the expression “ordinary hours”. This refers to the hours of work performed by an employee for which they are to be paid at the ordinary rate for the industrial agreement/the minimum adult wage.
Usually hours of work performed have to fall within certain time periods or occur on certain days to be defined as “ordinary hours”.
Overtime
An industrial agreement will usually include an overtime clause. Overtime occurs where an employee performs work outside of their ordinary hours of work. It is important for an employer to review such clauses thoroughly to ensure that employees receive an overtime payment whenever it is owed.
The actual rate of pay applicable for overtime varies from agreement to agreement. Generally, overtime tends to apply at the rate of either time and a half or double time.
Penalty rates
Many industrial agreements will include higher rates of pay applicable to work performed on a Saturday. Such time is still classed as ordinary hours of work.
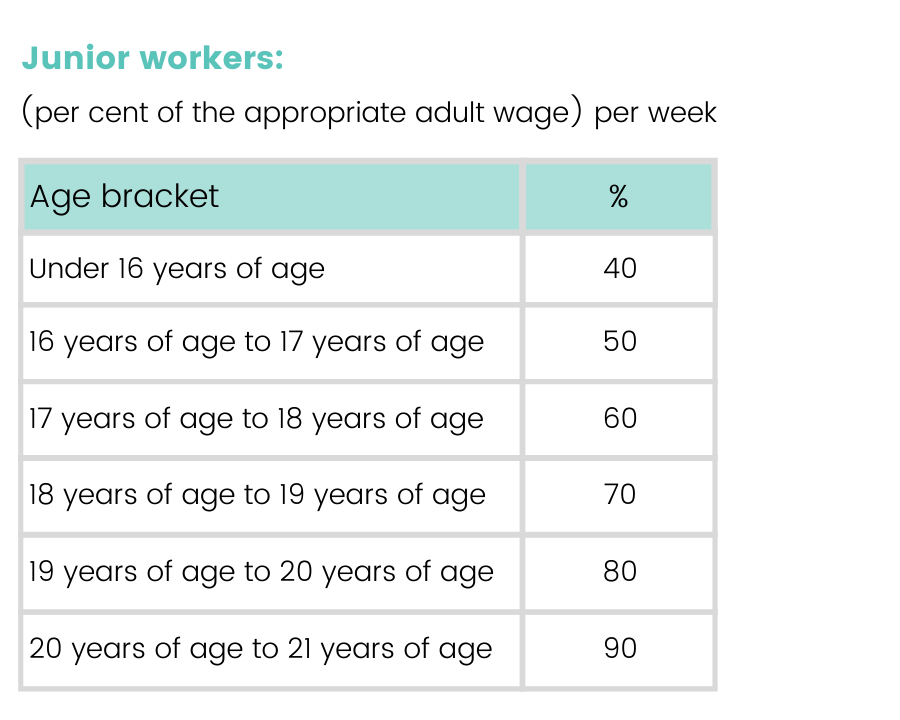
Junior rates
You should also be aware that depending upon the age of your employees, they may only be entitled to be paid a percentage of the applicable wages for an adult employee under the industrial agreement.
What resources are available to ensure that I meet my wage obligations towards employees?
The Department of Mines, Industry Regulation and Safety operate the Wageline service which can assist you with questions you have concerning employee pay, applicable pay rates, employee hours of work and leave entitlements.
Agreements and contracts of
As an employer, it is important to be aware of how the industrial agreement that covers your business interacts with contracts of employment used for your employees.
It is important to understand that an employee’s entitlements as outlined in an industrial agreement cannot be removed by an employment contract. If an employee is entitled to receive a penalty rate for work performed on a Sunday under the enterprise agreement, they cannot “sign away” this entitlement under a standard contract of employment.
What can an employment contract do?
Properly used, employment contracts play a crucial role in ensuring wage and record-keeping compliance. The use of employment contracts achieves the following:
Explains when and how an employee is to be paid
An employment contract should confirm how frequently an employee is to be paid (i.e. weekly, fortnightly, monthly) subject to the award. It should also explain if an employee is to be paid:
- at an hourly rate in line with the industrial agreement;
- at a higher hourly rate than the industrial agreement; or
- a salary that compensates the employee for their industrial agreement entitlements (see the next module for information concerning things to consider when using a salary).
Ensures compliance with record-keeping obligations
Many industrial agreements include requirements that an employee is informed in writing as to the industrial agreement they are covered by, their classification under that industrial agreement, their type of employment and when their hours of work will be performed. The inclusion of such information in an employment contract ensures that this information is recorded and retained in one place.